How to select the best 3D Filament for your 3D printer
Which filament should I choose? Is ABS or PLA better? What is the difference between a normal PLA and PLA 3D850? Can I print PETG with my printer?
These and many other similar questions are what our customers ask us, and they are very common doubts in 3D printing, in this article we will try to answer them in a clear way.
Types of filament
There are a multitude of filaments on the market today, and there are often new variants of those already known. In this article we are going to treat it taking into account its base material.
It is advisable to know all the types of materials available, the advantages and disadvantages of each, and thus be able to select the ideal material for each application. In some cases there will be more than one material that can perform the same task as they are very versatile.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid)
The PLA is the most used material, it is easy to print and the scale of its production makes it increasingly economical and accessible. Within the PLA we find different types:
- Standard PLA, does not have special characteristics, it is generally offers a glossy finish, defined, precise, rigid and fragile pieces, therefore it is not recommended for mechanical pieces that work under important loads, but it is recommended for decorative and functional pieces that do not receive blows or important loads. In addition, this is usually the most economical material.
https://www.hta3d.com/en/filamento#/material-pla-a16-vPLA/
- Modified PLA, there are other types of PLA on the market that have been modified to improve their performance, generally increasing the ease of printing and their resistance to heat and impact. Within this range we find:
- PLA 3D850: It is the material that we recommend as a starter have improved its properties in 3 main lines: thermal resistance, impact resistance and ease of printing. In addition, the price remains very tight and only slightly higher than normal PLA.
These properties also make it great as a commonly used material, for kit parts, and for mechanical parts under moderate stress.
https://www.hta3d.com/en/filamento#/material-pla-ingeo-3d850-a16-vPLA
- PLA 3D870: this is a further step in the line of improvement of the PLA, in this case in addition to significantly increase the improvements of the 3D850, it is optimized for an annealing process (110ºC for about 20 minutes), this process rearranges the molecular structure of the material making it even more resistant to temperature and impact.
It is therefore an ideal material for industrial applications and production of small series of parts in specific sectors.
https://www.hta3d.com/en/filamento#/material-pla-ingeo-3d870-a16-vPLA%20Ingeo%203D870/
- PLA 3D850: It is the material that we recommend as a starter have improved its properties in 3 main lines: thermal resistance, impact resistance and ease of printing. In addition, the price remains very tight and only slightly higher than normal PLA.
- Standard PLA, does not have special characteristics, it is generally offers a glossy finish, defined, precise, rigid and fragile pieces, therefore it is not recommended for mechanical pieces that work under important loads, but it is recommended for decorative and functional pieces that do not receive blows or important loads. In addition, this is usually the most economical material.
- ABS: It has been during the first years of the popularization of 3D printing the most used material, thanks to its easy availability. It is considered an engineering plastic for its excellent mechanical properties such as high impact resistance and flexibility.
Its main difficulty is the thermal contraction of the material and the poor bond between layers, however manufacturers are gradually improving this point, remaining an interesting option for small parts that are subjected to high temperatures.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/abs-1-75mm-c89/
- PETG: It is a material that is becoming increasingly popular. It combines the ease of printing of PLA with the mechanical properties of ABS. It is therefore ideal for most mechanical applications.
It has some disadvantage over PLA and ABS, as it tends to accumulate small "balls" during printing which may then leave some small stain or imperfection on the part. And ABS is still superior in resisting high temperatures.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/petg-1-75mm-c110/
- HIPS: It has excellent mechanical properties, similar to ABS. But it stands out for its high resistance to atmospheric agents and UV rays, being very interesting for outdoor applications where the sun and climate can easily degrade other materials. It is also soluble in limonene so it can be used as a support material.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/material-hips-a16-vHIPS/
- Flexible: Within flexible materials we find a very high variety, since there are different degrees of hardness and flexible materials can be made with very different properties.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/flexible-c106/
- TPU / TPE: these are the main materials used to make flexible filaments, they have excellent mechanical properties, high resistance to impact and abrasion. TPU can be found unmodified offering outstanding properties but limited flexibility.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/material-tpu-a16-vTPU/
- Formulas: We also find different formulations such as FilaFlex and eFil filaments. These manufacturers also offer different degrees of hardness in their filaments. Remember that the more flexible a material is, the more difficult it is to print with it. We therefore recommend starting with the intermediate flexibility formulas such as mediun flex and eFil-HT.
https://www.hta3d.com/es/filamento#/material-tenaflex,material-efil,material-efil-ht-a16-vTENAFLEX,eFil,eFil-HT/
- TPU / TPE: these are the main materials used to make flexible filaments, they have excellent mechanical properties, high resistance to impact and abrasion. TPU can be found unmodified offering outstanding properties but limited flexibility.
Other considerations:
Colour
The colour is achieved by adding a dye to the base material, this dye slightly modifies the properties of the material, in general it is usually recommended light colors because they are the least impact have, most materials have a "natural" color without dye, where it usually offers the best performance.
This has evolved over time and each time the differences are smaller depending on the color. In 2014 some colours had different working temperatures, with differences of up to 20ºC in some cases.
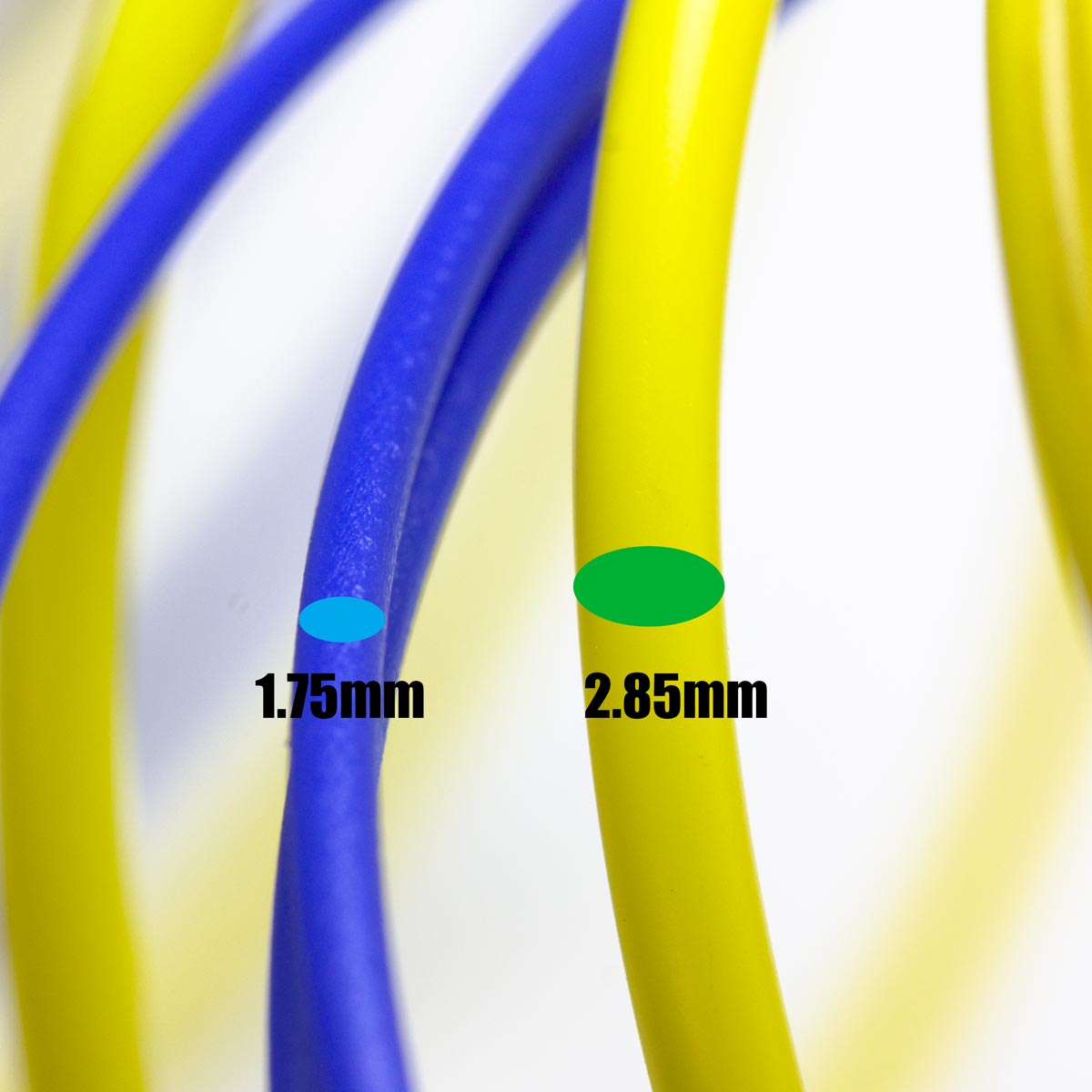
Thickness
The filament of diameter 1,75 has been imposed on the filament of 3mm by many factors:
- It is easier to handle, especially on rigid filaments such as PLA, as being thinner it has less tendency to split, the reels can be smaller and gives less problems when placing it on the printer.
- Having a larger contact surface for the same amount of material, it melts more easily and at a more uniform temperature.
- It needs less force to be extruded, so extruders can be lighter, compact and simple.
- It is more precise, since for the same amount of material, a greater linear movement is generated than with 3mm.
- It is a unique standard, the nominal size is 1.75 regardless of the manufacturer. The 3mm filament has been divided into two types, 2.85 (the most popular) and 3mm (almost completely disused).
Despite all these advantages, the 3/2.85mm filament has a significant advantage with the very flexible material. Because the thicker the filament, the better it works, it is one of the reasons why it is still manufactured. If you need flexible filament 2,85 you can contact us to make a personalized order.








1 Comment(s)
Saben cuando se podrán realizar pedidos? Estoy con la impresora parada y no puedo ayudar a la causa...
Estamos aceptando pedidos, muchas gracias.
Leave a Comment