
The functioning and the connections of a stepper motor are simple concepts deeply.
There are different types of stepper motors. In 3D printing the most used are "Hybrid Stepper Motor", with two phases and 4 connections; which combines the features of "Variable Reluctance Motor" and "Permanent Magnetizing Motor"
In this video we can see the types os stepper motors, as so as its functioning:
As we have seen, the stepper motor has two phases with two connections per phase: four connections in total. We can see them at the diagram:
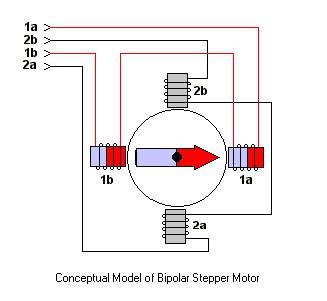
Which position must have each the connection?
We must connect according to the indicated on RAMPS board: 2211, although 1122 will work also.

How can I identidy the phases?
Each phase has continuity, so with a multimeter we can measure the continuity in the motor connection. Every connector has continuity with the other connector that corresponds with its phase and not with the others.
What happens if I cross the phases of the motor?
The motor will vibrate, but it won't move. The advantage is that this kind of mistake doesn't damage the electronic and it is easey to identify.
What happens if I change the orientation of any phase?
The stepper motor will move in the opposite direction.
How can I change the spinning orientation?
The easiest way to do it is to connect it the other way round. You can do it from the firmware also.
How can I make the motor get less warmed?
You can decrease the current intensity and thus, the motor power.
The motor hasn't enough power and my printer misses steps, what can I do?
In Prusa 3D printers, the intensity is usually adjusted between 0,2 A and 0,4 per motor; being possible to lift this value to the nominal power of the motor. One of the options is increasing the current assigned to the motor. Also you can modify the acceleration and/or checking that mechanically everything is right.
Do you have any other question? We will answer it!







8 Comment(s)
Hola buenas poes llevo 1 año con esto de las impresoras 3d y ahora que me an empezado a dar fallos me estoy adentrando mas en la electronica i el firmware y eso. Mi pregunta es como puedo conectrar un motor que compre nuevo para el extursor porque es como si no lo detectase. Y e probado con el pronterface pero no me conecta con la impresora aun teniendo el cable usb a la placa.un saludo y muchas gracias
Hola Jose, habría que ver detenidamente el caso, ya que puede ser cualquier cosa, desde configuración de firmware hasta físicamente el cableado del motor, contacta con nosotros usando este enlace: https://www.hta3d.com/es/contacto indicando el número de pedido del motor y electrónica, y nuestro soporte técnico te ayudará.
Buenas, tengo una impresora 3D tipo prusa con un extrusor mk8 y hotend e3d v6. Cuando comienzo a imprimir,el filamento corre correctamente, pero al cabo de unos minutos de impresión, el engranaje de motor extrusor empieza a saltarse pasos (haciendo un sonido de click ) y el filamento deja de correr por el tubo de teflon,llegando a ir hacia detrás el filamento. Como podría solucionar este problema???? Es un problema del muelle?? El engranaje está correctamente apretado también, puede ser un problema de tensión?? Como puedo ajustarlo??\r\n\r\nMuchísimas gracias por leer mis mensaje y espero que su respuesta me ayude!!!
En este caso te aconsejo contactar con el fabricante o vendedor de la impresora en cuestión. Al saltarse pasos cabe pensar que le falta potencia, pero puede ser otra cosa. Los extrusores Mk8 con polea de color dorado son en general muy malos al no tener una correcta refrigeración ni barrera térmica, nosotros nunca los hemos puesto en catálogo por ello.
Esta obstruido el conducto que conecta el hotend con el extrusor. Cambia la boqulla por una nueva, el esparrago por otro de igual medida y el teflón que lleva dentro, si es con capricorn, mejor.
Installez le http custom
donde conectar pulsador de inicio de apertura y cierra manual
Que driver se puede utilizar ?
Dependiendo de la configuración hay muchísimos drivers disponibles, en esta categoría puedes encontrar nuestro stock: https://www.hta3d.com/es/componentes/electronica/controladores
Buenas tardes, tengo un extensor de rango al cual se le quemo el motor paso a paso, le compre otro (24byj48), el toma tiene los hilos de color diferente a la de la caja reguladora, lo conecto y no me funciona correctamente. ¿Me podrian ayudar?
El color de los hilos puede cambiar de un modelo a otro, lo más importante es identificar las fases y comprobar el sentido de giro. Puedes escribirnos al formulario de contacto con el número de pedido para ayuda personalizada.
Tienen bipolares de cinco bobinas tipo
PK599AE-N10
Compre a un particular Un SERVO DRIVE HIBRIDO HBS86H con display digital es decir el selector de micro interruptore fue reemplazado por este sistema digital nuevo para mi ,he buscado informacion y no he encontrado nada y en el mercado tampoco se encuentra nada , el problema es que no encuentro manual ni instrucciones para la programcion y lo peor es que las instrucciones que bienen por lo ragular en el exterior del drive estan en CHINO , alguien me puede ayudar ? le estaria altamente agradecido .
Atentamente : rangelzo ( Rafael Angel )
Leave a Comment